Untreated ADHD can trigger academic setbacks, job instability, mental‑health issues, substance abuse, and even legal problems. This guide explains the long‑term risks and offers steps to get help.
Read MoreADHD Consequences: Understanding the Real Impact
When you hear the term ADHD consequences, the range of effects that attention‑deficit/hyperactivity disorder can have on daily life, work, and relationships. Also known as ADHD outcomes, it encompasses everything from missed deadlines to strained friendships. The picture becomes clearer when you consider ADHD symptoms, impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention as the driving force. Those symptoms don’t stay in a vacuum – they ripple into Adult ADHD, the continuation of ADHD into adulthood, where the stakes shift from classroom grades to career growth. Likewise, the link between Academic performance, grades, focus, and learning outcomes in school settings and early‑life ADHD symptoms is a classic cause‑and‑effect chain. Finally, ADHD treatment, medication, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle adjustments can modify or even break these chains, showing how intervention directly shapes the overall picture.
Why the Impact Matters
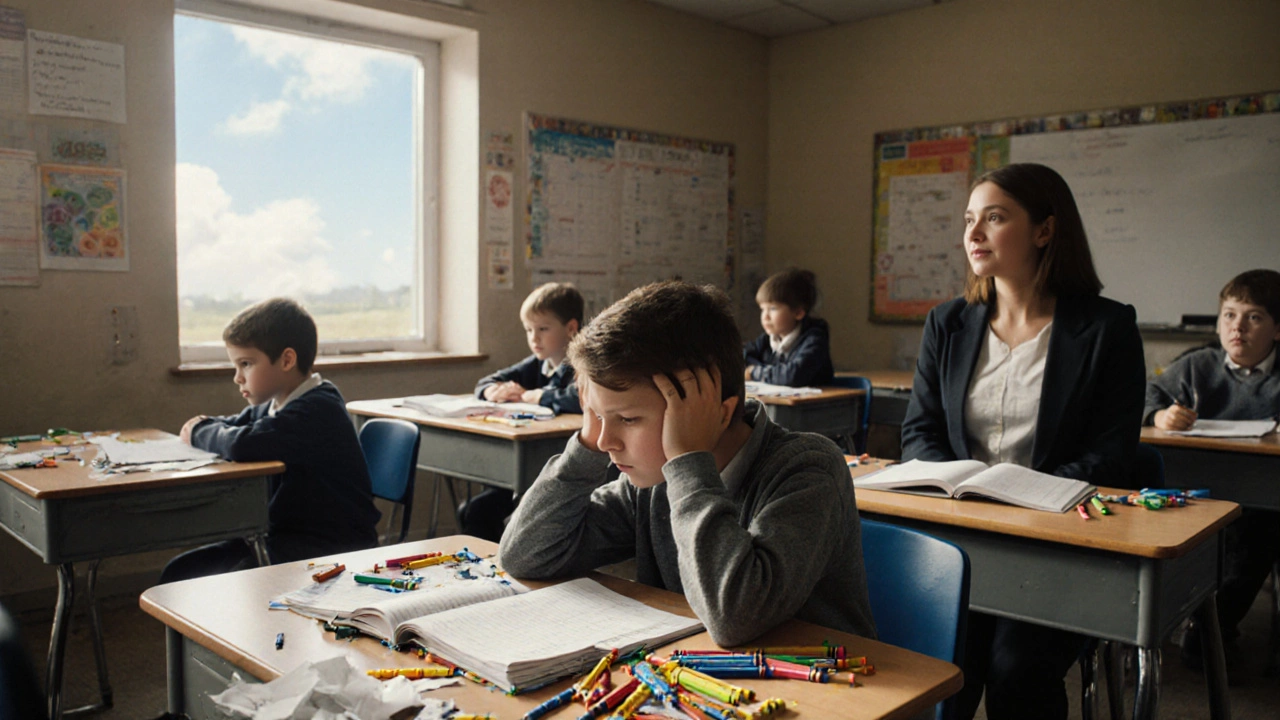
Understanding the ADHD consequences is more than an academic exercise; it’s a roadmap for everyday decisions. Imagine a teen who can’t sit through a lesson because of hyperactivity – the immediate result is a lower test score, which then feeds into reduced confidence and a higher risk of dropping out. That is a direct symptom‑to‑consequence pathway that many families witness. In the workplace, an adult with unmanaged impulsivity may interrupt meetings, miss project milestones, or struggle with time management, leading to promotion stalls or job changes. These real‑world outcomes illustrate the semantic triple: ADHD symptoms influence academic performance, academic challenges affect career prospects, and effective ADHD treatment can mitigate negative consequences. When you map these links, you see where a small change – like a structured routine or a low‑dose stimulant – can ripple into big improvements across life domains.
Beyond school and work, the social fabric feels the strain. Relationships often suffer when one partner forgets plans or reacts impulsively during arguments. Health‑wise, untreated ADHD is tied to higher rates of accidents, substance use, and even chronic stress‑related conditions. Recognizing these patterns helps you prioritize which consequence to address first. If academic performance is the biggest pressure point, you might focus on behavioral coaching and classroom accommodations. If workplace stability is the goal, time‑blocking tools and medication adjustments become key. In every case, the overarching theme is that ADHD treatment isn’t a one‑size‑fits‑all fix; it’s a set of strategies that target the specific consequences you’re facing. Below you’ll find articles that dive deeper into each of these areas, from symptom management tips to real‑life recovery stories, giving you a toolbox to turn knowledge into action.