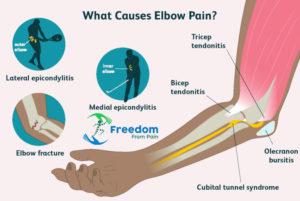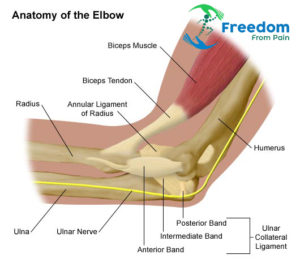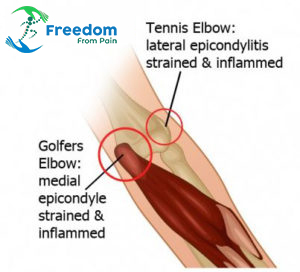
Elbow pain is often caused by an injury, overuse or a fall, or related to a sports injury; however, it can be the result of a medical condition such as arthritis.
Types of Elbow Pain :
Elbow arthritis : The elbow joint is the point where the humerus, the radius, and the ulna come together and meet. In the elbow joint, the ends of the bones have a smooth shiny surface called joint articular cartilage. This allows them to slide freely over each other without grinding or causing friction. This articular cartilage can become damaged by arthritis. When it does, the individual will begin to experience pain and discomfort in the joint.
Elbow Bursitis : Bursitis is a painful condition that happens when you have inflammation of a bursa. Bursae are small fluid-filled pads (or sacs) found near your joints. They act like cushions, reducing friction by allowing tendons and muscles to move smoothly over bones and other structures.
Tennis Elbow : Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) is a condition in which there is pain where the tendons from the forearm extensor muscles attach to the bony prominence on the outside of the elbow (lateral epicondyle).