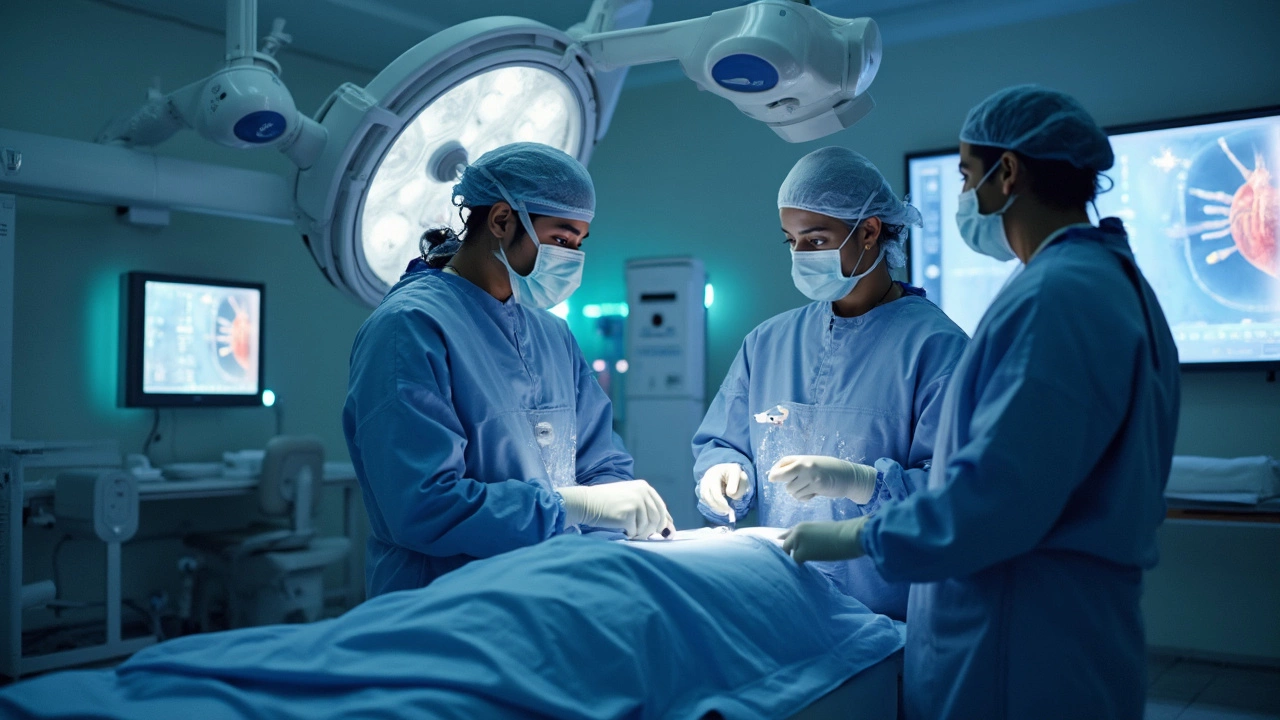
Wondering if open-heart surgery still involves breaking ribs? Explore the fascinating advances in heart surgery techniques that have rendered many traditional practices obsolete. Discover the modern alternatives now available, the risks involved, and what to expect during recovery. An essential read for anyone curious about cutting-edge medical procedures and heart health.
Read MoreModern Surgery – What’s New, How It Affects Pain, and What You Need to Know
If you’ve ever worried about going under the knife, you’re not alone. Today’s operating rooms look a lot different from the ones in the old textbooks. Robots, tiny cameras, and smarter anesthesia are turning scary procedures into smoother experiences. In India, hospitals are fast‑adopting these tools, which means less tissue damage, lower blood loss, and—most importantly—much less pain after the operation.
Let’s break down the big changes. First, there’s minimally invasive surgery. Instead of a large cut, surgeons use a few millimeter‑sized ports and a camera called a laparoscopy or an endoscope. This approach is common for gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and even some joint surgeries. Second, robot‑assisted surgery is gaining ground in cardiac and urologic procedures. The robot doesn’t replace the surgeon; it just gives steadier hands and better 3‑D vision. Finally, advances in pain‑blocking techniques—like nerve blocks and long‑acting local anesthetics—let patients go home with just a mild ache instead of a pounding headache.
How Modern Surgery Cuts Pain
Traditional open surgery often leaves you with swelling, bruising, and a heavy dose of opioids to manage the hurt. Modern methods attack that problem from three angles. First, the smaller incisions mean fewer nerves are cut, so the body’s own pain signals stay lower. Second, many surgeons now use Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols, which combine early feeding, gentle mobilization, and targeted analgesia. The result? Patients report lower pain scores on the first day after surgery.
Third, advanced anesthesia blends regional blocks—like an epidural for knee replacements—with ultra‑short‑acting drugs that wear off quickly. This combo can keep you comfortable without the grogginess that comes from heavy sedation. In practice, you might hear a patient say, “I was up and walking by evening,” instead of the old “I was glued to the bed for days.”
Recovery Tips After Modern Procedures
Even with lighter pain, your body still needs time to heal. Here are a few practical steps that work for most modern surgeries:
1. Move early. Gentle stretching or short walks within the first 24‑48 hours keeps blood flowing and reduces stiffness. Follow your surgeon’s instructions—most ERAS plans encourage a few steps right away.
2. Eat right. Protein‑rich foods, plenty of fluids, and a balanced mix of carbs help rebuild tissue. Some hospitals provide nutrition plans that include soups, fruits, and light proteins right after the operation.
3. Follow the pain plan. Take prescribed medications exactly as directed. If you’re using a nerve block, you might only need a simple over‑the‑counter pain reliever once the block fades.
4. Watch for warning signs. Redness, increasing swelling, or a fever higher than 38°C (100.4°F) can indicate infection. Contact your doctor immediately if anything feels off.
5. Keep follow‑up appointments. Modern surgeons often schedule a quick check‑in a week after surgery to tweak pain meds or adjust physical therapy. Skipping it can delay your return to normal activities.
Putting these steps together can shave days off your recovery timeline and keep you from relying on strong painkillers. Most patients find they’re back to work or daily chores within two to three weeks for many minimally invasive procedures—much faster than the month‑plus recovery of older techniques.
Bottom line: Modern surgery isn’t just about high‑tech gadgets. It’s about a whole ecosystem that aims to reduce pain, speed up healing, and let you get back to life faster. If you’re facing an operation, ask your surgeon about minimally invasive options, ERAS protocols, and the specific pain‑management plan they’ll use. Knowing what to expect gives you confidence and helps you play an active role in a smoother, less painful recovery.